Astronomers have discovered the tiniest star present in the Milky Way Galaxy which is hardly as big as the ringed planet Saturn.
Also Read: "Alien ice" is seen forming on Earth for first time! Here are top 7 interesting facts about it
This star is dubbed EBLM J0555-57Ab and according to the scientists it is the smallest star discovered so far, a Gizmodo report stated. The star was discovered by researchers at Cambridge's Cavendish Laboratory and Institute of Astronomy.
"Our discovery reveals how small stars can be," Alexander von Boetticher, a Master's student at Cambridge's Cavendish Laboratory and Institute of Astronomy and the lead author of the study, explained in a statement.
"Had this star formed with only a slightly lower mass, the fusion reaction of hydrogen in its core could not be sustained, and the star would instead have transformed into a brown dwarf," Boetticher added.
Here are 7 facts to know about the tiniest star in the Milky Way Galaxy:
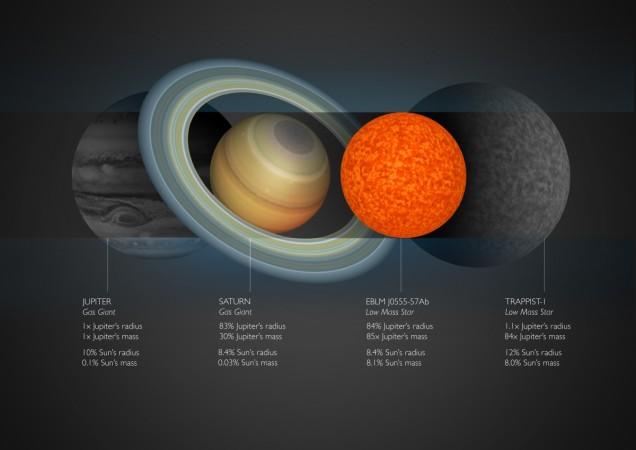

- This star is located 600 light-years away from Earth and is defined as one of the densest stellar objects discovered in the solar system so far according to a study called "A Saturn-size low-mass star at the hydrogen-burning limit" published by Astronomy & Physics.
- EBLM J0555-57Ab was discovered by a group of researchers who were a part of the team that found the TRAPPIST-1 system -- another tiny and dim star that has seven planets. This tiny star was first noticed when it flew by another giant parent star.
- Though it is defined as the tiniest star in the Milky Way Galaxy, large telescope could spot it from the Southern Hemisphere.
- The gravitational pull at the surface of the star is found to be three hundred times stronger than on Earth.
- According to the findings by the researchers, this star has just enough mass to result in the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium, like in the Sun.
- The size of this star is said to be big enough to be qualified as a full-fledged star.
- This little star was found by WASP -- a planet-finding experiment -- which is run by the Universities of Keele, Warwick, Leicester and St Andrews.








