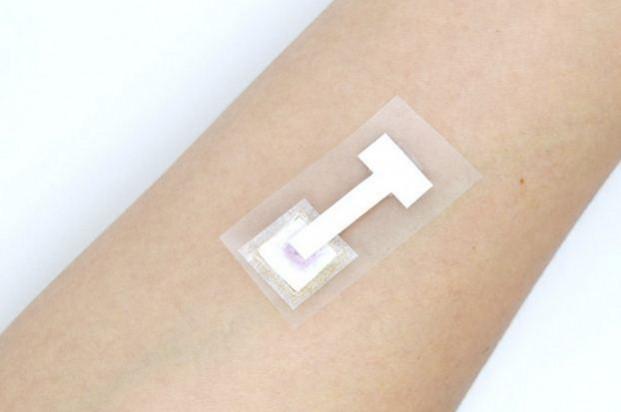
Japanese researchers have developed a novel compact patch that can detect the presence of Covid antibodies non-invasively within three minutes.
The team from the University of Tokyo focused on the interstitial fluid (ISF) -- located in the epidermis and dermis layers of human skin -- to detect the anti-Covid IgM/IgG antibodies.
The findings, published in the journal Scientific Reports, showed that the new antibody-based method rapidly and accurately helps in the detection of SARS-CoV-2.
The predominant Covid detection method to date collects samples by swabbing the nose and throat. However, the application of this method is limited by its long detection time (4-6 hours), high cost, and requirement for specialised equipment and medical personnel, particularly in resource-limited countries.
An alternative and complementary method for the confirmation of Covid-19 infection involves the detection of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies.
Testing strips based on gold nanoparticles are currently in widespread use for point-of-care testing in many countries. They produce sensitive and reliable results within 10-20 minutes, but they require blood samples collected via a finger prick using a lancing device.
This is painful and increases the risk of infection or cross-contamination, and the used kit components present a potential biohazard risk.
"To develop a minimally invasive detection assay that would avoid these drawbacks, we explored the idea of sampling and testing the ISF. Although the antibody levels in the ISF are approximately 15-25 per cent of those in blood, it was still feasible that anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM/IgG antibodies could be detected and that ISF could act as a direct substitute for blood sampling," said lead author Leilei Bao from the Institute of Industrial Science at the varsity.
After demonstrating that ISF could be suitable for antibody detection, the researchers developed an innovative approach to both sample and test the ISF.

"First, we developed biodegradable porous microneedles made of polylactic acid that draws up the ISF from human skin. Then, we constructed a paper-based immunoassay biosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies," Beomjoon Kim, senior author, said.
Results from the lab tests showed that by integrating these two elements, the compact patch was capable of on-site detection of the antibodies within 3 minutes, Kim said.
This novel detection device has great potential for the rapid screening of Covid-19 and many other infectious diseases that are safe and acceptable to patients. It holds promise for use in many countries regardless of their wealth, which is a key aim for the global management of infectious disease, the team said.