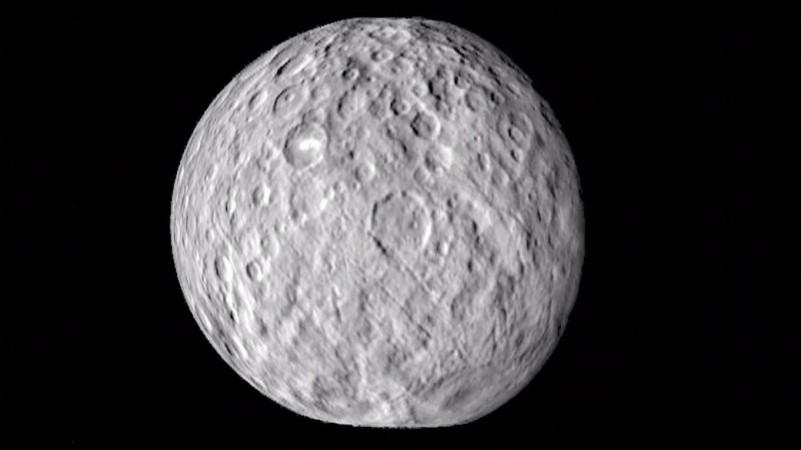
Space researchers recently discovered the presence of water on dwarf planet Ceres. The shallow sub-surface, as well as the surface of this dwarf planet, points towards direct evidence about the presence of water ice.
Present in the asteroid belt located between Mars and Jupiter, Ceres is the biggest object, with a diameter of 945 kilometers, present near the sun. This planet was doubted to have large amounts of water on it. The water present on the planet is estimated to be equal to 30 percent of its entire mass.
As per the proof accumulated by the researchers, the water ice present on Ceres comprises of the rock present on the surface of the planet. Extra concentrated patches of ice have been found on Ceres too. The dwarf planet has even been spotted spreading water vapour with the help of NASA's Dawn probe, which was launched in 2007.
The results of the latest findings reveal the distribution of hydrogen on the planet, which can help understand the presence of water on Ceres.
The planet's water content separated from the rock content to form an ice crust on the planet, according to the findings. The existence of water in large amounts on the planet points towards predictions that water ice can exist within a metre of the planet's surface for billions of years. These findings have been presented in a detailed study.
NASA's Dawn spacecraft, which is presently orbiting the planet, created a global map with the help of an instrument present on it called Gamma Ray and Neutron Detector (GRaND). Two types of articles are identified by this device: gamma rays, which are very high energy light, and neutrons, particles which help in creating atoms.
A mist of debris particles, which includes neutrons and gamma rays, is formed when high-energy particles called cosmic rays collide with the dwarf planet's surface. The debris, which is generated, is capable of providing data about the chemical compositions of Ceres' surface till a certain depth with the help of the gamma rays and neutrons.
The researchers analysed the GRaND data of up to 1 meter or 3 feet below the planet's surface and found that it comprises of iron, potassium and nitrogen. As per the authors, detecting the presence of water molecules beneath the surface couldn't be done directly with the help of this device, but it can be concluded with the help of the data collected, the researchers revealed.
Using computer models is one of the ways how the evolution of this dwarf planet is recreated. This helps in bringing forward the fact how these elements and water are presently distributed on the surface of the planet.
On comparing the models, it was disclosed that
- The water ice present near both the poles was more concentrated.
- The water ice concentration was found to be much lesser near its equator.
- The new research also revealed that the water ice present on and under Ceres' surface is equal to almost 30 percent of its total mass.

The map of Protoplanet Vesta, which is another celestial companion of Ceres present in the asteroid belt, was compared with the map of Ceres. It was found the hydrogen levels present on Ceres was 100 times more than that present on Vesta. Also, the element was found to be present in a more even manner on the surface, which points towards water being the largest component present on the dwarf planet's composition, said Thomas Prettyman, principal investigator for GRaND, in a press conference on December 15, 2016, at the annual meeting of American Geophysical Union in San Francisco.
"If you look at the elemental composition of Ceres, it bears some resemblance to the carbonaceous contrite meteorites," Prettyman said, as per a space.com report.
"But there are differences that support the idea that ice and rock that came together and formed Ceres actually separated in the interior and were redistributed by processes like convection," he added.
There is a possibility of the ocean beneath Ceres' surface to be extremely salty with scanty water content, as disclosed by Carol Raymond, the deputy principal investigator of the Dawn mission. Though the new results of the study indicate the water being stored near the planet's surface in form of ice deposits.

The journal Nature stated that there is a rare concentrated deposit of surface ice on a crater of the planet, which is located in a region covered in permanent shadow, as quoted by space.com. Such craters are referred to as "cold traps".