For the first time in history, a spacecraft has touched the Sun as NASA's Parker Solar Probe has finally entered the upper atmosphere – the corona – and sampled particles and magnetic fields from there.
The new milestone marks one major step for Parker Solar Probe and one giant leap for solar science. Just as landing on the Moon allowed scientists to understand how it was formed, touching the very stuff the Sun is made of will help scientists uncover critical information about our closest star and its influence on the solar system.
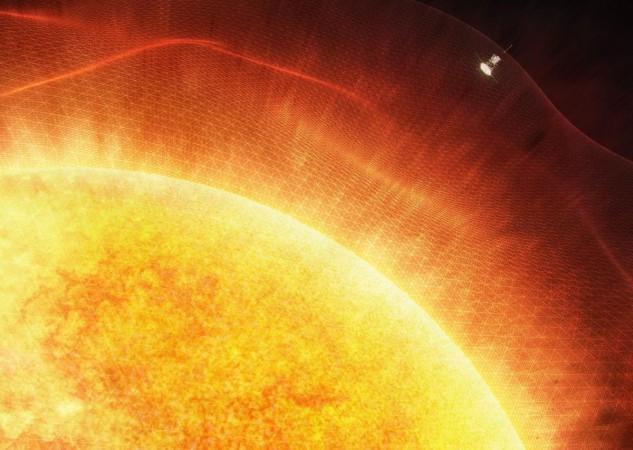

"Parker Solar Probe "touching the Sun" is a monumental moment for solar science and a truly remarkable feat," said Thomas Zurbuchen, the associate administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington.
As it circles closer to the solar surface, Parker is making new discoveries that other spacecraft being far away failed to see, including from within the solar wind – the flow of particles from the Sun that can influence us at Earth.
In 2019, Parker discovered that magnetic zig-zag structures in the solar wind, called switchbacks, are plentiful close to the Sun. But how and where they form remained a mystery. Halving the distance to the Sun since then, Parker Solar Probe has now passed close enough to identify one place where they originate: the solar surface.
The first passage through the corona – and the promise of more flybys to come – will continue to provide data on phenomena that are impossible to study from afar, say astronomers.
Closer Than Ever Before
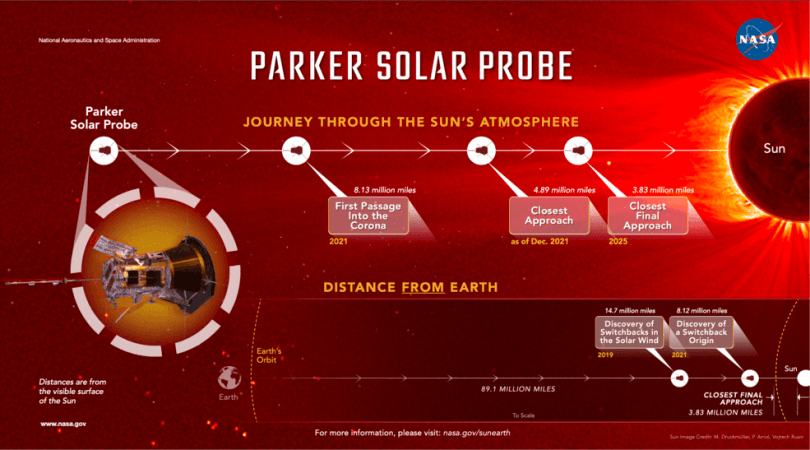
Parker Solar Probe launched in 2018 to explore the mysteries of the Sun by traveling closer to it than any spacecraft before. Three years after launch and decades after first conception, Parker has finally arrived.
Unlike Earth, the Sun doesn't have a solid surface. But it does have a superheated atmosphere, made of solar material bound to the Sun by gravity and magnetic forces. As rising heat and pressure push that material away from the Sun, it reaches a point where gravity and magnetic fields are too weak to contain it.
That point, known as the Alfvén critical surface, marks the end of the solar atmosphere and beginning of the solar wind. Until now, researchers were unsure exactly where the Alfvén critical surface lay. Based on remote images of the corona, estimates had put it somewhere between 10 to 20 solar radii from the surface of the Sun – 4.3 to 8.6 million miles.
Parker's spiral trajectory brings it slowly closer to the Sun and during the last few passes, the spacecraft was consistently below 20 solar radii (91 percent of Earth's distance from the Sun), putting it in the position to cross the boundary – if the estimates were correct.
On April 28, 2021, during its eighth flyby of the Sun, Parker Solar Probe encountered the specific magnetic and particle conditions at 18.8 solar radii (around 8.1 million miles) above the solar surface that told scientists it had crossed the Alfvén critical surface for the first time and finally entered the solar atmosphere.
"We were fully expecting that, sooner or later, we would encounter the corona for at least a short duration of time," said Justin Kasper, lead author on a new paper about the milestone published in Physical Review Letters, and deputy chief technology officer at BWX Technologies and University of Michigan professor. "But it is very exciting that we've already reached it."
Into the Eye of the Storm
During the flyby, Parker Solar Probe passed into and out of the corona several times. This is proved what some had predicted – that the Alfvén critical surface isn't shaped like a smooth ball. Rather, it has spikes and valleys that wrinkle the surface. Discovering where these protrusions line up with solar activity coming from the surface can help scientists learn how events on the Sun affect the atmosphere and solar wind.
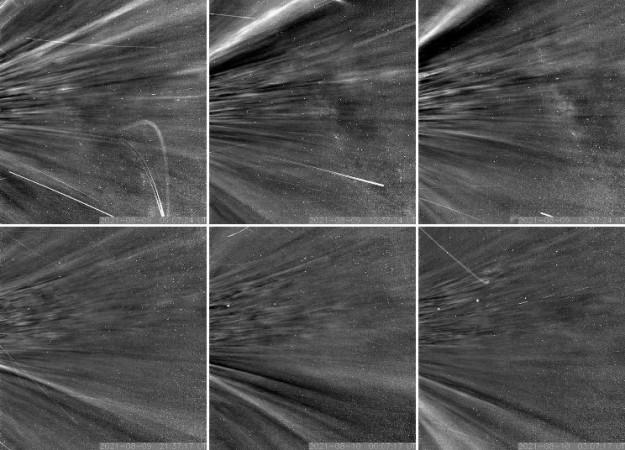
As Parker Solar Probe passed through the corona on encounter nine, the spacecraft flew by structures called coronal streamers. At one point, as Parker Solar Probe dipped to just beneath 15 solar radii (around 6.5 million miles) from the Sun's surface, it transited a feature in the corona called a pseudostreamer, which consists of massive structures that rise above the Sun's surface and can be seen from Earth during solar eclipses.
The first passage through the corona, which lasted only a few hours, is one of many planned for the mission. Parker will continue to spiral closer to the Sun, eventually reaching as close as 8.86 solar radii (3.83 million miles) from the surface. Upcoming flybys, the next of which is happening in January 2022, will likely bring Parker Solar Probe through the corona again.
Narrowing Down Switchback Origins
Even before the first trips through the corona, some surprising physics was already surfacing. On recent solar encounters, Parker Solar Probe collected data pinpointing the origin of zig-zag-shaped structures in the solar wind, called switchbacks. The data showed one spot that switchbacks originate is at the visible surface of the Sun – the photosphere.
By the time it reaches Earth, 93 million miles away, the solar wind is an unrelenting headwind of particles and magnetic fields. But as it escapes the Sun, the solar wind is structured and patchy. In the mid-1990s, the NASA-European Space Agency mission Ulysses flew over the Sun's poles and discovered a handful of bizarre S-shaped kinks in the solar wind's magnetic field lines, which detoured charged particles on a zig-zag path as they escaped the Sun. For decades, scientists thought these occasional switchbacks were oddities confined to the Sun's polar regions.
In 2019, at 34 solar radii from the Sun, Parker discovered that switchbacks were not rare, but common in the solar wind. This renewed interest in the features and raised new questions: Where were they coming from? Were they forged at the surface of the Sun, or shaped by some process kinking magnetic fields in the solar atmosphere?
The new findings, published in the Astrophysical Journal, finally confirm one origin point is near the solar surface. The clues came as Parker orbited closer to the Sun on its sixth flyby, less than 25 solar radii out.
Understanding where and how the components of the fast solar wind emerge, and if they're linked to switchbacks, could help scientists answer a longstanding solar mystery: how the corona is heated to millions of degrees, far hotter than the solar surface below.
Now that researchers know what to look for, Parker's closer passes may reveal even more clues about switchbacks and other solar phenomena. The data to come will allow scientists a glimpse into a region that's critical for superheating the corona and pushing the solar wind to supersonic speeds.
Parker Solar Probe is part of NASA's Living with a Star program to explore aspects of the Sun-Earth system that directly affect life and society.





!['Had denied Housefull franchise as they wanted me to wear a bikini': Tia Bajpai on turning down bold scripts [Exclusive]](https://data1.ibtimes.co.in/en/full/806605/had-denied-housefull-franchise-they-wanted-me-wear-bikini-tia-bajpai-turning-down-bold.png?w=220&h=138)



