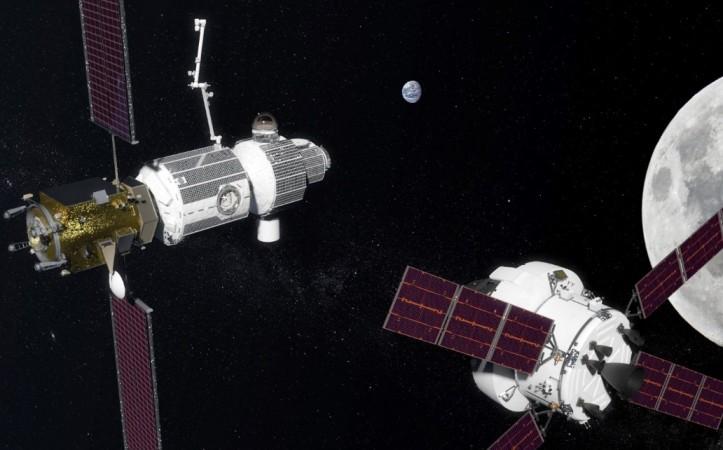
NASA's plan to set up a space station in orbit near the moon is getting a major push as the space agency will award the first contract for its construction. It is intended to serve as NASA's staging area for deep space exploration and study.
The Gateway is also expected to eventually become a transit point for Mars explorers as well, notes a report by Bloomberg. By early 2019, the first contracts floated out for this project will be for components that make up power and propulsion, and it will be followed by habitat components, notes the report.
The first launch for this project is expected to happen by 2022. By 2025, a basic platform could be orbiting the Moon. A four-astronaut crew on 30-day missions will be sent up first, says William Gerstenmaier, Associate Administrator at NASA. Apart from being a gateway to deep space, this space station could also serve as a way for NASA to send people back to Moon. Late last year, the space agency's focus was once again, under the current Trump Administration, shifted from Mars to the Moon.
Water near the Lunar surface could also be mined and used to manufacture propellant for rockets traveling further into space, notes the report. The Moon's gravity can also be used as a way to help slow down spaceships traveling at enormous speeds from Mars and make it possible for spaceships to carry out safe Earth re-entry procedures.
"We want to understand orbital mechanics around the moon" a little better, far from the Earth's deep gravity well, said Gerstenmaier. "Doing things in this region, where gravity isn't such a big driver ... is a different way of operating."
NASA called on five companies last year to study and begin developing solar-electric propulsion systems, notes the report. The reason for this is because to facilitate deep space exploration, propulsion has to triple in capacity when compared to current systems, notes the report. The lunar space station is also expected to make use of such a propulsion system.
This Luna gateway will be lifted to Moon orbit using the Orion spacecraft being built by Lockheed Martin in collaboration with ESA, notes the report.









!['Had denied Housefull franchise as they wanted me to wear a bikini': Tia Bajpai on turning down bold scripts [Exclusive]](https://data1.ibtimes.co.in/en/full/806605/had-denied-housefull-franchise-they-wanted-me-wear-bikini-tia-bajpai-turning-down-bold.png?w=220&h=138)