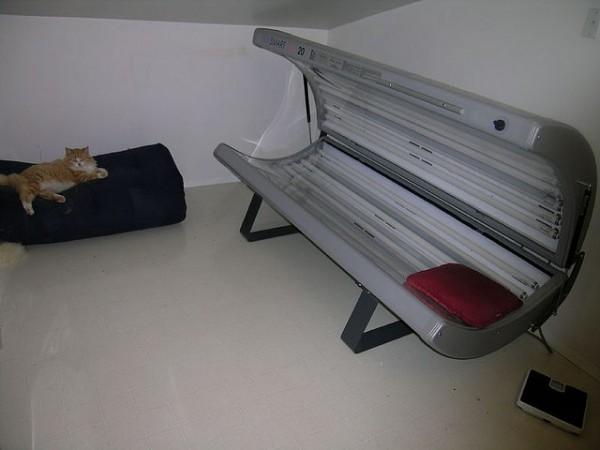
Early exposure to indoor tanning can increase the risk of being diagnosed with skin cancer at a young age, a new study says.
The study, reported in the online edition of Pediatrics, analysed the hidden risks associated with indulging in indoor tanning at a young age and an early onset of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), a type of cancer that starts in the outer layer of the skin known as epidermis.
It is found more common in areas highly exposed to sun including face, neck, scalp, trunk and legs. It can appear as a waxy or pearly white bump, in patches -mostly brown or flesh coloured- on back and chest or as a white and waxy scar, according to the experts from Mayo Clinic in US.
For the study, researchers from the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth College in the United States looked at 657 basal cell carcinoma patients and compared them to 452 people without cancer. During the study, the participants provided information about the type of indoor tanning device they used including sunlamps, tanning beds and booths and the total time they spent under the sun at childhood.
Use of tanning lamp at an early age was directly linked to development of BCC at a young age. People who started using indoor tanning before age 20 were found at greater risk of being diagnosed with BCC before age 50, Live Science reported.
"Indoor tanning products produce 10 to 15 times as much UV radiation as the midday sun," the researchers said in an American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) news release.
"Our findings suggest early exposure to indoor tanning increases the risk of early development of BCC," the authors, while concluding their study, wrote. "They also underscore the importance of counseling adolescents and young adults about the risks of indoor tanning and for discouraging parents from consenting minors to this practice."
Following are some factors that increase the risk of basal cell carcinoma, as provided by Mayo Clinic and Medline Plus:
- Prolonged exposure to tanning booths or sun
- Having blue, green or grey eyes
- Possessing blond or red hair
- Early exposure to x-ray or radiation during treatments
- Having a fair skin
- Possessing more number of moles
- History of sunburns in the past
- Daily exposure to sun light
- Gender- men are at higher risk than women
- Having a family history of skin cancer
- Arsenic exposure