After releasing the anti-phishing update to Gmail for Android, Google has finally rolled out the critical security patch to iOS-based Gmail for iPhones and iPads.
Earlier this year, a serious security loophole was discovered in the Android and PC versions of Gmail, wherein several users received suspicious emails with Google Doc attachment, which was later found to be riddled with phishing malware.
Also read: OnePlus 3, 3T series meet OnePlus 2 fate; Will OnePlus 5 get Android P?
Taking note of the seriousness of the issue, Google had released a statement saying that they have started an investigation and also urged users to block emails from unknown senders and flag them as phishing emails.
Soon after the conclusion of the inspection, Google released an anti-phishing update to Gmail for Android. Now, the company has made it available to iOS.
Once updated, whenever you click on a suspicious link in a message, Gmail will show a warning to help you keep your account safe.
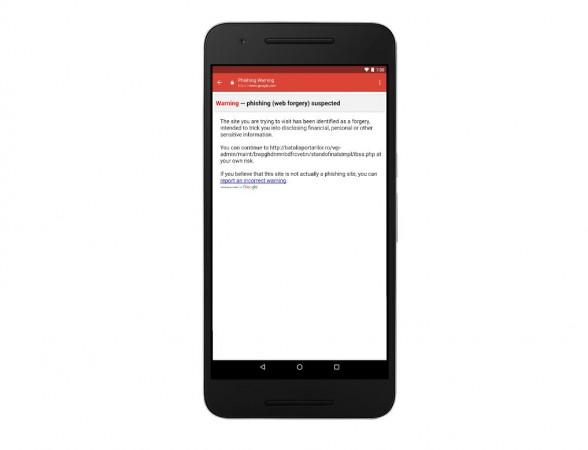
"Going forward, when you click on a suspicious link in a Gmail message on your iPhone or iPad, we'll show the warning below. We recommend that you use caution before proceeding because the link is likely unsafe. Only proceed if you're confident there's no risk," Google said in a statement.
What is phishing and how you can safeguard from it?
For the uninitiated, phishing is a very serious fraudulent practice of sending emails feigning to be from reputable companies or a person. Once they gain your confidence, they will persuade the unsuspecting user to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.
Sometimes, the user will be asked to press a link and he/she unsuspectingly click it, which then take them to an unreliable websites and lure them in to installing malware by popping warning messages on their PC (or any smart devices) screen that there is virus in the system and need to download anti-virus firmware immediately.
Again, fearing damage to their devices, naive individuals unsuspectingly click the download button and end installing a malware. Then, hackers take control of victims device and remote scan for sensitive information like financial data including bank accounts, credit/debit card details and sometimes personal photos and later sell them online or later call the victim to demand ransom for not to circulate their intimate photos in the public domain.
Phishing has become the most serious cyber threat today, as it has the potential to hit finances of large multinational companies to a commoner like us.

With more and more people entering the online ecosystem, cases of data theft are increasing faster than before. So, we urge our readers to be more vigilant whenever they get emails from unknown persons and if they are convinced that the sender is not related to them or their work. Tag the mail as spam and block them.
Follow us @IBTimesIN_Tech on Twitter for latest updates on Google and Apple products.

















