
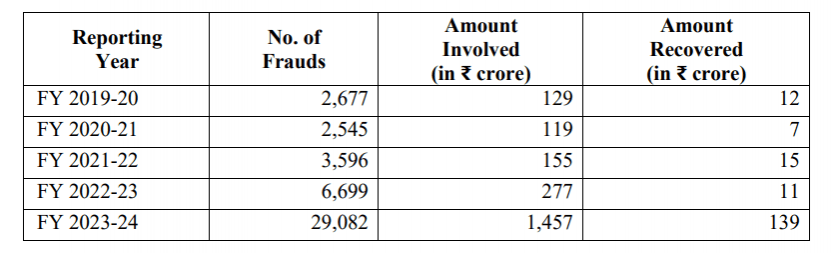
Although concerned departments have launched aggressive campaigns to educate people about cyber fraud, the digital scammers have looted as many as Rs 1,447 crore from gullible people through 29028 cases in the financial year 2023-24.
The number of digital fraud cases in the country has been steadily rising, as fraudsters continue to adopt various methods to deceive people. In response to a question in the Rajya Sabha, Minister of State for Finance, Pankaj Chaudhary, revealed that in the financial year 2019-20, there were 2,677 reported cases of digital fraud. This figure increased to 6,699 in the financial year 2022-23 and further skyrocketed to 29,028 cases in 2023-24.
In the financial year 2019-20, digital fraud involved a total of Rs 129 crore, of which only Rs 12 crore was recovered by authorities. By the financial year 2023-24, the amount looted through digital fraud had surged to Rs 1,457 crore, with only Rs 139 crore successfully recovered.

The Minister also stated that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) does not maintain specific data on digital fraud cases. As per the Ministry of Home Affairs, 'Police' and 'Public Order' are state subjects according to the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India, making States and Union Territories (UTs) primarily responsible for the prevention, detection, investigation, and prosecution of crimes, including cybercrime, through their Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs). The Central Government supports these efforts through advisories and financial assistance under various capacity-building schemes.
On July 15, 2024, the RBI issued three revised Master Directions on Fraud Risk Management for Regulated Entities (REs). Additionally, the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) undertakes various measures to promote the safe use of digital technologies and prevent cyber fraud, including issuing alerts and advisories and conducting cybersecurity mock drills to assess organizations' cyber security posture and preparedness.
To assist citizens in reporting cyber incidents, including financial frauds, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has launched the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (www.cybercrime.gov.in) and the National Cybercrime Helpline Number (1930). Customers can also report financial fraud on the official customer care websites or at bank branches.

Initiatives taken by the government to create awareness
To spread awareness against cyber-crimes, the Government has been taking various initiatives from time to time. These, inter alia, include cyber safety tips through social media accounts, publishing of a handbook for adolescents/students, publishing of 'Information Security Best Practices' for the benefit of government officials, organizing cyber safety and security awareness weeks in association with States/Union Territories, etc.
In addition to these, RBI and Banks have also been organizing awareness campaigns through the dissemination of messages on cyber-crime through short SMS, radio campaigns, and publicity on the prevention of 'cyber-crime'. Further, RBI has been conducting electronic-banking awareness and training (e-BAAT) programmes that focus, inter alia, on awareness about fraud and risk mitigation.

















