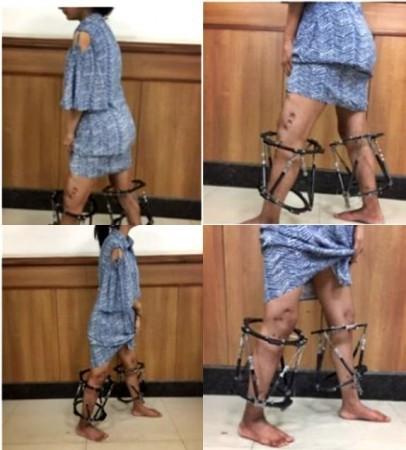
In a groundbreaking medical achievement, a 19-year-old girl from Himachal Pradesh, Ayesha, has had her bowlegs, or crooked legs as they are commonly referred to in medical parlance, straightened using a novel AI-assisted technique. This remarkable feat was accomplished by the medical team at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi, led by Senior Deformity Correction Surgeon, Manish Dhawan.
Bowlegs is a condition where the legs appear bent outward, even when the ankles are together. In Ayesha's case, both her legs and thighs were bent outward, a condition she was born with. This physical deformity had a profound impact on her life, especially during her school years. It led her to become increasingly introverted, grappling with feelings of inferiority, and struggling to engage socially due to her condition.
The medical team at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital employed a unique AI-assisted technique to correct Ayesha's deformity. The technique involved the use of an Ilizarov fixator and six-axis correction software. The Ilizarov technique is a surgical procedure that involves an orthopedic external fixator applied to the limb to reconstruct, reshape, or lengthen bones, usually of the limb.
The Ilizarov fixator, as explained by Dr. Manish Dhawan, is a Hexapod, which has six legs and can move in any direction. The Hexapod circular fixator consists of two rings connected by six obliquely oriented struts. These fixators are then paired with computer software, which the surgeon can manipulate to control the desired correction speed and direction. This is not a frame but a unique universal software-based deformity correction unit.
The software plays a crucial role in the deformity correction process. It simulates the correction by drawing the bone contour that shows the initial position of the mobile bone fragment and the expected final position, as calculated by the software. This AI-assisted technique was instrumental in correcting Ayesha's leg deformities effectively and also helped her increase her height by 2 inches.
The surgical process was both physically and emotionally demanding, lasting two to three months. However, Ayesha's resilience saw her through this challenging period. Today, she is back on her feet and working at a national bank in Uttar Pradesh, a testament to the success of this novel AI-assisted technique.
This remarkable medical feat was reported on June 13, with the article published on June 14, 2024. It marks a significant milestone in the field of orthopedic surgery and AI-assisted medical procedures. The successful application of AI in this case opens up new possibilities for treating similar conditions in the future.
Historically, the Ilizarov technique has been used to treat various orthopedic conditions, including limb length discrepancies, non-unions, and complex fractures. However, the integration of AI into this technique is a relatively new development. This successful case of Ayesha demonstrates the potential of AI-assisted techniques in orthopedic surgery and could pave the way for more such procedures in the future.
In conclusion, the successful correction of Ayesha's bowlegs using an AI-assisted technique is a significant achievement in the field of orthopedic surgery. It not only offers hope to individuals suffering from similar conditions but also underscores the potential of AI in revolutionizing medical procedures. As we move forward, it will be interesting to see how AI continues to shape the future of medicine, offering new possibilities and hope for patients like Ayesha.

















