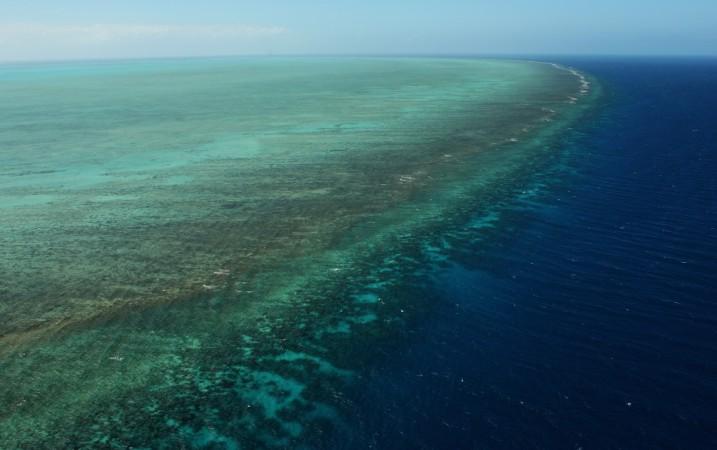
Australia's Great Barrier Reef, the world's largest coral reef system, could suffer a bleaching event every two years by 2034 under the current level of greenhouse gas pollution, according to a study published on Thursday.
"Limiting temperature rise above pre-industrial levels to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius is critical for the survival of reefs worldwide," said the report called "Lethal Consequences: Climate Impacts on the Great Barrier Reef", published by the Climate Council, reports Efe news.
According to the study, 70 percent of coral reefs will be at risk of long-term degradation by 2100 if the global temperature rises by 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. An increase in global temperature of 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels would put 99 percent of the corals at risk.
The experts also indicated that the two consecutive coral bleaching events on the Reef in 2016 and 2017 have led to mass coral mortality. Nearly 30 percent of the coral reefs died after the unprecedented bleaching event in 2016, the worst phenomenon ever recorded on the Great Barrier Reef, which is a Unesco World Heritage Site.
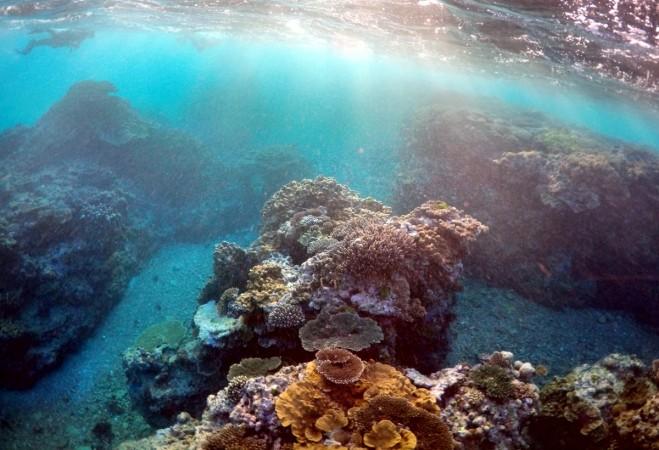

In 2016, the Great Barrier Reef registered the highest sea surface temperature in February, March and April since it was first recorded in the early 1900s. It also recorded coral mortality in that same period and in the following eight months due to a high water temperature related to climate change.
The future of coral reefs around the world depends on the measures taken to mitigate the impacts of climate change as well as the immediacy of the actions taken to reduce greenhouse gas pollution levels in the coming years and decades, according to the study.
The Great Barrier Reef, home to 400 types of corals, 1,500 species of fish and 4,000 varieties of molluscs, contributes some AUD$6.4 billion ($4.8 billion) a year to Australia's economy.
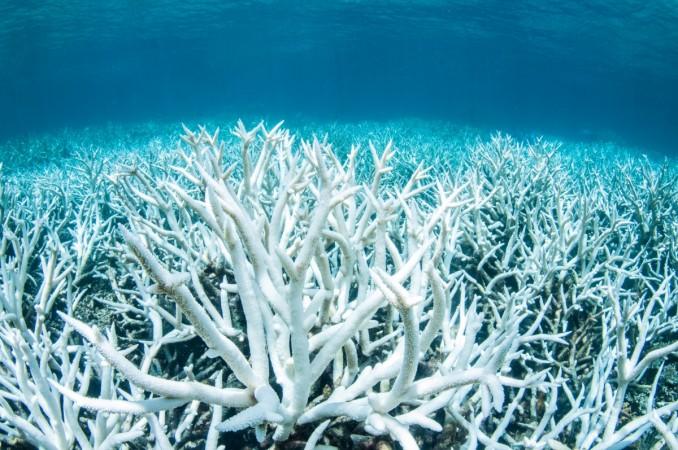

The world's largest coral ecosystem began to deteriorate in the 1990s due to the double impact of sea warming and the increase of its acidity as a result of the increasing level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.